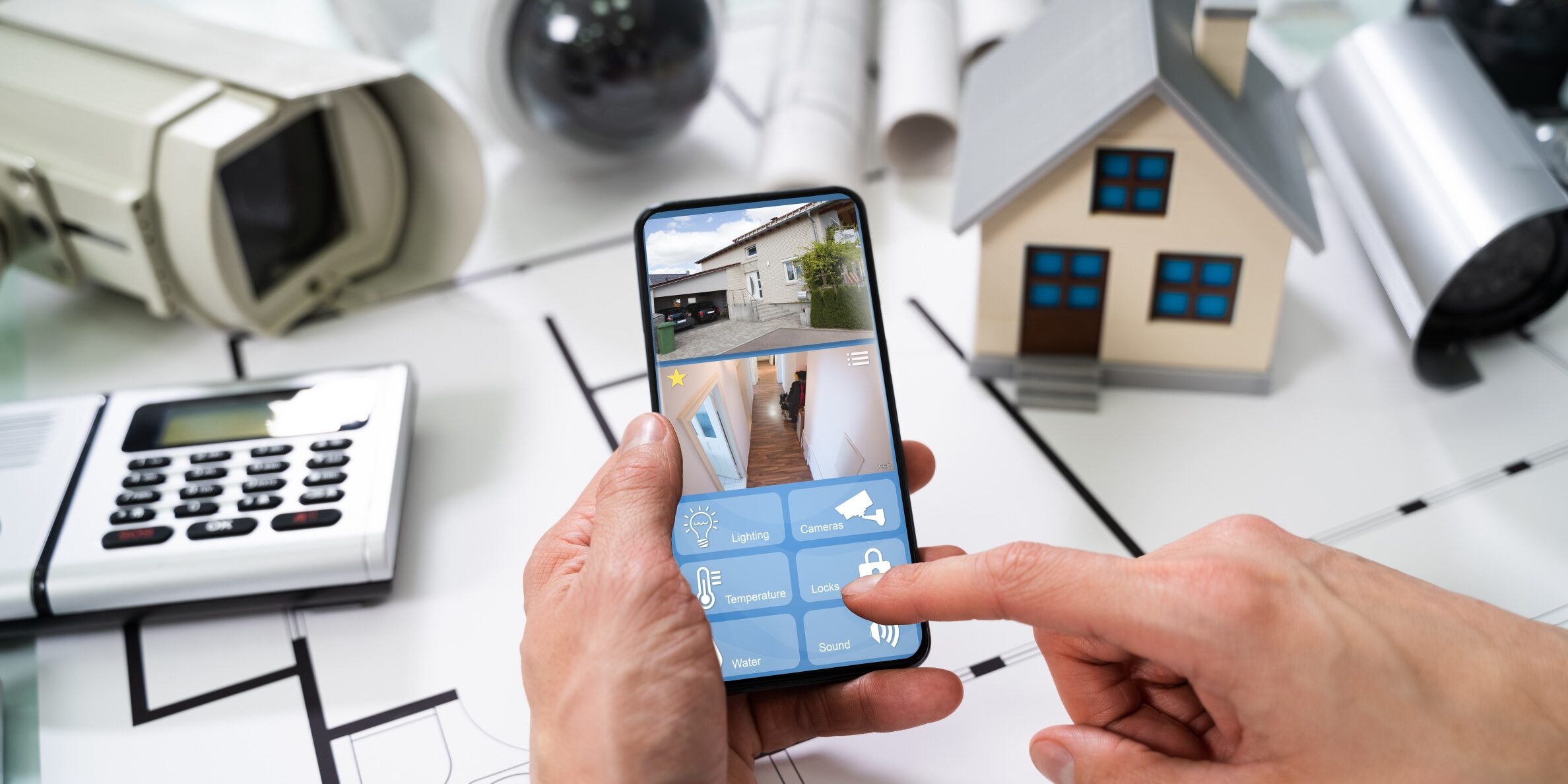
How to Self-Monitor My Home Security System
Self-monitoring your home security system allows you to personally oversee the safety of your home. Here are some measures to help you effectively self-monitor your home security system:
1. Choose a reliable security system
Select a home security system that offers self-monitoring capabilities. Look for a system that provides alerts, notifications, and remote access to the system through a mobile app or a web portal.
2. Install security cameras
Place security cameras strategically around your property to monitor different areas. Ensure they cover entry points like doors, windows, and driveways. Position cameras at a height and angle that provides a clear view of the surroundings.
3. Set up motion sensors
Motion sensors detect movement in designated areas and trigger alarms. Install them near vulnerable entry points or key areas of your home, such as hallways or rooms with valuable belongings.
4. Enable door/window sensors
Door and window sensors detect when they are opened or closed. Install them on all accessible doors and windows. They will alert you if any entry point is breached.
5. Configure remote access
Connect your security system to your home network and configure remote access through a mobile app or a website provided by your security system provider. Follow the instructions issued by the manufacturer to set up and link your system to the remote access platform.
6. Test your system
Regularly test your security system to ensure all the parts function correctly. Trigger alarms, test motion sensors, and verify if the notifications are received on your mobile device or computer.
7. Set up alerts and notifications
Configure your security system to send you alerts and notifications for specific events. It may include alarm triggers, motion detection, or door/window breaches. Ensure the notifications are sent to your preferred device, such as your smartphone or email.
8. Establish emergency contacts
Identify emergency contacts, including local authorities, neighbors, or friends who can aid you. Share this information with trusted individuals.
9. Monitor notifications and alerts
Regularly check your smartphone, email, or other designated devices for notifications and alerts from your security system. Pay attention to any unexpected or suspicious activity.
10. Respond to alerts promptly
When you receive an alert indicating a potential security breach, assess the situation immediately. If necessary, contact the appropriate authorities or emergency services. Inform your emergency contacts if needed.
11. Keep your system up to date
Regularly update your security system’s software and firmware to ensure it has the latest features, bug fixes, and security patches. Check for updates from the manufacturer and follow their installation instructions.
12. Maintain your system
Keep your security system in good working order. Replace batteries in sensors and cameras as needed, clean cameras to maintain clear visibility, and ensure all components are correctly connected and functioning.
Remember, to self-monitor your home security system means you’ll be responsible for monitoring and responding to potential threats. If you’re away from home for prolonged periods or prefer professional monitoring, consider subscribing to a professional monitoring service offered by security companies.
Benefits of Self-Monitoring My Home Security System
Self-monitoring your home security system can offer several benefits. Here are some advantages of self-monitoring:
-
Cost-effectiveness
Self-monitoring your home security system is often more cost-effective than subscribing to a professional monitoring service. You could save money in the long run by eliminating monthly monitoring fees.
-
Increased control and flexibility
With self-monitoring, you have complete control over your security system. You can personalize and adjust settings according to your preferences. Additionally, you can arm or disarm the system remotely and receive notifications directly on your smartphone or other devices.
-
Immediate awareness of security events
Self-monitoring lets you receive real-time alerts and notifications directly on your mobile device or computer. You are instantly aware of any security events, such as alarm triggers, motion detection, or door/window breaches, enabling you to respond promptly.
-
Quick response to emergencies
With self-monitoring, you can immediately assess the situation and take appropriate action in an emergency. You can contact the authorities, alert neighbors or emergency contacts, and provide the necessary information to ensure a swift response.
-
Reduced false alarms
Self-monitoring enables you to verify the cause of an alarm before contacting emergency services. It helps lessen false alarms and prevent unnecessary dispatches, potentially saving you from fines or penalties imposed by local authorities.
-
Privacy and data control
Self-monitoring gives you more control over your data and privacy. You can choose how and where your security system data is stored, ensuring it is handled securely and by your preferences.
-
Customized notifications
Self-monitoring allows you to customize the types of notifications you receive. You can receive alerts only for specific events, such as particular sensor triggers or areas of your property. This customization helps minimize unnecessary notifications and lets you focus on relevant security events.
-
Increased awareness and peace of mind
You better understand your property’s security status by monitoring your home security system. Knowing you protect your home and loved ones, this heightened awareness can provide peace of mind.
-
Integration with smart home devices
Many self-monitoring systems integrate with other smart home devices, such as smart locks, lights, and thermostats. This integration allows you to create automated routines and enhance home security and convenience.
It’s important to note that self-monitoring requires a proactive approach and the ability to respond promptly to security events. Professional monitoring services may better fit your security needs if you prefer a more hands-off method or are frequently away from home.
Disadvantages of Self-Monitoring My Home Security System
While self-monitoring your home security system can have its advantages, there are also several potential disadvantages to consider:
-
Limited availability
Self-monitoring means you are always responsible for monitoring your security system. If you are away from the device or unable to respond to notifications promptly, you may not be able to address security events promptly.
-
Reliance on personal response
With self-monitoring, responding to security events falls solely on you. If you cannot take immediate action or miss an alert, you may delay addressing potential threats or emergencies.
-
Lack of professional expertise
Professional monitoring services employ trained personnel who are experienced in handling security events. With self-monitoring, you may not have the same level of expertise or knowledge in assessing and responding to security situations.
-
False alarms
Self-monitoring increases the possibility of false alarms, which can be triggered by various factors such as pets, environmental conditions, or technical glitches. Dealing with false alarms can be time-consuming and may cause unnecessary stress.
-
Limited backup and redundancy
Professional monitoring services often have backup systems and redundancies to ensure continuous monitoring, even during power outages or system failures. With self-monitoring, if your devices or internet connection fail, you may lose the ability to monitor your security system effectively.
-
Lack of professional escalation
 Professional monitoring services can quickly escalate the case to the appropriate authorities or emergency services in certain situations, such as a confirmed intrusion or fire. With self-monitoring, you may need to personally coordinate and communicate with emergency services, which can add complexity and potentially delay response times.
Professional monitoring services can quickly escalate the case to the appropriate authorities or emergency services in certain situations, such as a confirmed intrusion or fire. With self-monitoring, you may need to personally coordinate and communicate with emergency services, which can add complexity and potentially delay response times.
-
Emotional and psychological impact
Constantly monitoring your home security system and being solely responsible for its protection can create added stress and anxiety. Some individuals may struggle to maintain constant vigilance, leading to emotional fatigue.
-
Maintenance and upkeep
Self-monitoring requires regular maintenance and upkeep of your security system. It includes testing components, replacing batteries, updating software, and ensuring the proper functioning of devices. Neglecting these tasks can result in gaps in your security coverage.
-
Privacy and data management
Self-monitoring offers greater control over your data. However, it also means you are responsible for managing and securing that data. You must protect your devices, network, and storage solutions to prevent unauthorized access.
When deciding whether self-monitoring is the right approach for your home security system needs, you must weigh these potential disadvantages against your personal preferences, lifestyle, and availability.
Things to consider before self-monitoring home security system
Before deciding to self-monitor your home security system, consider the following factors:
1. Availability and Responsiveness
Self-monitoring requires you to be available and responsive to security alerts and notifications. Assess your ability to consistently monitor your system and promptly respond to potential security events. Self-monitoring may not be your best option if you routinely travel or have a busy lifestyle that may hinder your ability to react swiftly.
2. Technical Knowledge
Evaluate your technical skills and comfort level when managing a home security system. Self-monitoring often involves setting up and configuring devices, troubleshooting technical issues, and ensuring proper connectivity. Professional monitoring may be better if you lack technical knowledge or prefer a more hands-off approach.
3. Risk Assessment
Consider the security risks specific to your property and location. Evaluate factors such as crime rates in your area, the vulnerability of entry points, and the presence of valuable assets. If you reside in a neighborhood with a higher risk of break-ins or have valuable possessions that require enhanced protection, professional monitoring might provide an added layer of security.
4. False Alarms
Assess the potential for false alarms in your home. Factors such as pets, environmental conditions, or system malfunctions can trigger false alarms. Determine if you can effectively handle and manage false alarms without causing undue stress or inconvenience.
5. Emergency Response
Consider your ability to handle emergencies independently. In break-ins, fires, or medical emergencies, you’ll be responsible for contacting emergency services, providing information, and coordinating the response. Evaluate your confidence and capability in handling such situations effectively.
6. Backup and Redundancy
Assess the reliability of your internet connection, power supply, and backup systems. Self-monitoring relies on consistent connectivity and functioning devices. Ensure you have backup solutions to handle power outages or network disruptions that could impact your ability to monitor the system.
7. Privacy and Data Management
Reflect on your privacy concerns and ability to manage and secure your security system data. Self-monitoring means you have control over your data, but it also involves securing it. Evaluate your willingness and capacity to implement appropriate security measures to secure your data from unauthorized access.
8. Support and Maintenance
Consider the level of support and maintenance required for your security system. Evaluate if you are comfortable handling regular testing, device updates, battery replacements, and troubleshooting. Neglecting maintenance tasks can lead to gaps in your security coverage.
9. Cost Analysis
Compare self-monitoring costs versus professional monitoring services. Consider initial equipment costs, ongoing maintenance expenses, and any potential discounts or insurance benefits associated with professional monitoring. Determine if the cost savings of self-monitoring outweigh the benefits of professional monitoring.
By carefully examining these factors, you can decide whether self-monitoring suits your home security needs. Choosing an approach that aligns with your capabilities, lifestyle, and the level of security you require is essential.

Summary
In conclusion, self-monitoring is a home security system with several benefits and advantages but specific considerations and potential drawbacks. Here’s a summary:
Benefits of self-monitoring:
1. Cost-effectiveness by eliminating monthly monitoring fees.
2. Increased control and flexibility over your security system.
3. Immediate awareness of security events through real-time alerts and notifications.
4. Quick response to emergencies by personally assessing and taking appropriate action.
5. Privacy and data control with the ability to manage and secure your data.
6. Customized notifications to minimize unnecessary alerts.
7. Integration with smart home devices for enhanced security and convenience.
Considerations and potential drawbacks of self-monitoring:
1. Limited availability and the need for prompt responsiveness to security events.
2. Lack of professional expertise and escalation capabilities in handling security situations.
3. Possibility of false alarms and the need to manage and address them.
4. Limited backup and redundancy, potentially impacting monitoring during system failures.
5. Emotional and psychological impact from constant vigilance and responsibility.
6. Maintenance and upkeep requirements to ensure the system’s proper functioning.
7. Privacy and data management responsibilities to protect your data.
8. Need to assess the risks specific to your property and location.
9. Evaluation of emergency response capabilities in handling critical situations.
Ultimately, the decision to self-monitor your home security system should be based on your availability, technical knowledge, risk assessment, and preferences. Self-monitoring can be cost-effective and empowering if you have the time, ability, and eagerness to actively monitor and respond to security events. However, if you prefer professional expertise and around-the-clock monitoring or have specific security concerns, professional monitoring services may better fit your needs.








